What are Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)?
.png) |
| Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) |
LED stands for "Light Emitting Diode,".it is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electrical current passes through it. LEDs are used in a variety of devices, including lighting fixtures, electronic displays (such as those on televisions and smartphones), and automotive lighting.
LED(Light Emitting Diode) Symbol
The Symbol of LED is like a Diode. it contains an anode and cathode with an outgoing arrow .it shows light emitted when a current is flowing in the diode.
LED In Simple Circuit
The resistor is used to limit the current flowing through the LED to prevent it from burning out. The LED lights up when current flows through it in the correct direction (from positive to negative).
 |
| Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) |
Components Required
- LED (Light-Emitting Diode)
- Resistor (to limit current)
- The power source (such as a battery)
Working Principle of LED
Light-Emitting Diode is a semiconductor component that emits light when an electric current passes through it. An LED is made of semiconductor material, such as gallium arsenide (GaAs) or gallium phosphide (GaP).
The semiconductor material in an LED is doped to create a p-n junction, where "p" represents the positively charged region (containing excess holes) and "n" represents the negatively charged region (containing excess electrons).
When a voltage is applied across the p-n junction (by connecting the LED to a power source), electrons from the n-region move towards the p-region, and holes from the p-region move towards the n-region. This movement of charge carriers creates an electron-hole pair at the junction.
The electron from the n-region combines with the hole from the p-region at the junction. During this recombination process, energy is released in the form of a photon (light particle).
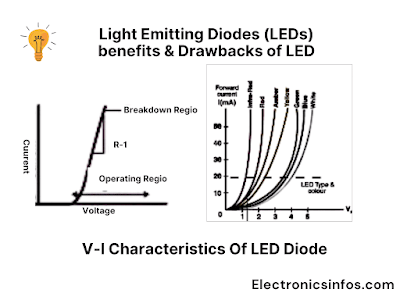
V-I Characteristics Of LED Diode
The V-I (voltage-current) characteristics of an LED (Light-Emitting Diode) describe how its voltage across the terminals (V) varies with the current passing through it (I).
Ratings Of LED
LEDs can be rated in several ways, including their brightness, colour temperature, and energy efficiency.
- LED brightness is measured in lumens, it is the total amount of visible light emitted by a light source. The higher the number of lumens, the brighter the LED.
- LED colour temperature is measured in Kelvin (K) which indicates the colour of the light emitted. Lower colour temperatures, around 2700K-3000K. it produces a warm, yellowish light similar to incandescent bulbs. higher colour temperatures, around 5000K-6500K, produce a cooler, bluish-white light.
- LED energy efficiency is measured in lumens per watt (lm/W). it indicates how much light is produced per unit of electrical power consumed.
- LEDs are much more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- it produces 70-80 lumens per watt.
Benefits of LED
In this article, we will explore the benefits and drawbacks of using LED lighting in your home. Here are some of the main advantages of LED lighting.
- LEDs are highly energy-efficient and use up to 75% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- LEDs have a much longer lifespan than traditional bulbs, with some LEDs lasting up to 25,000 hours.
- LEDs are free from toxic chemicals and are fully recyclable.
- LEDs are incredibly durable and resistant to shock, vibration, and external impacts.
- LEDs emit very little heat, making them safer to use and reducing the risk of fire hazards.
- LEDs are available in a wide range of colours, shapes, and sizes, allowing for more creative and innovative lighting designs.
- LEDs turn on instantly, with no warm-up time required.
- Many LED bulbs are dimmable, allowing for greater control.
Drawbacks of LED
- LEDs are initially more expensive than traditional bulbs.
- While the colour quality of LEDs has improved significantly in recent years, some people may still prefer the warm, yellow glow of incandescent bulbs.
- Not all LED bulbs are compatible with existing fixtures and dimmer switches.
- While LEDs are recyclable, the disposal process can be challenging.
LCD VS LED
Here are ten key differences between LCD and LED displays
- LCD displays use CCFL (cold cathode fluorescent lamp) backlighting technology, while LED displays use LED (light-emitting diode) backlighting technology.
- LED displays are thinner than LCD displays because they use a thinner backlighting system.
- LED displays use less power than LCD displays due to their more efficient backlighting system.
- LED displays can produce more accurate and vibrant colours than LCD displays.
- LED displays have higher contrast ratios than LCD displays, which means they can produce deeper blacks and brighter whites.
- LED displays generally have a longer lifespan than LCD displays.
- LED displays produce less heat than LCD displays because they use a more efficient backlighting system.
- LED displays have a faster refresh rate than LCD displays, which can make them better for gaming and other fast-moving content.
- LED displays have wider viewing angles than LCD displays, which means you can view the screen from more angles without experiencing colour distortion.
- LED displays are generally more expensive than LCD displays.
Applications Of LED
- LEDs are used in lighting fixtures for homes, businesses, and outdoor spaces.
- LEDs are used in automotive lighting, including headlights, brake lights, turn signals, and interior lighting.
- LEDs are used in electronic displays, including televisions, computer monitors, and smartphones.
- LEDs are commonly used in outdoor signs and billboards due to their brightness and energy efficiency.
- LEDs are used in traffic signals due to their energy efficiency and long lifespan.
- LEDs are used in medical devices, including photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photobiomodulation therapy (PBMT) devices.
- LEDs are used in indoor horticulture applications to provide supplemental lighting for plants.
- LEDs are commonly used in decorative lighting applications, including holiday lights, architectural lighting, and art installations.
- LEDs are used in aviation and marine lighting applications.
- LEDs are used in a variety of consumer electronics, including remote controls, digital clocks, and small handheld devices.
Conclusion
LEDs have several benefits, including energy efficiency, long lifespan, durability, and environmental friendliness. it makes them an attractive choice for various lighting applications.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is a Light Emitting Diode (LED)?
An LED is a semiconductor device. it emits light when an electric current passes through it.
What are the advantages of using LEDs?
LEDs have different advantages including
- energy-efficient,
- long lifespan,
- produce less heat,
- more durable compared to traditional incandescent bulbs.
Can LEDs be used for all types of lighting applications?
Yes, LEDs are versatile and can be used for a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, industrial, and automotive lighting.
What does the colour of an LED indicate?
The colour of an LED is determined by the material used in the semiconductor and the amount of energy gap between the electrons and holes.
Is it possible to dim LEDs?
Yes, many LEDs are dimmable, but it is important to ensure that the dimmer switch is compatible with the LED product.
What are some common applications of LEDs?
Common applications include indicator lights, display panels, automotive lighting, street lights, and increasingly, general-purpose illumination.
How do I choose the right LED for my needs?
Consider the brightness (lumens), colour temperature (Kelvin), energy consumption (watts), and the intended application when selecting an LED.
What is the lifespan of an LED?
The average lifespan of an LED is around 25,000 to 50,000 hours.
What advancements have been made in LED technology?
Recent advancements include the development of organic LEDs (OLEDs) and quantum dot LEDs (QLEDs).

%20Symbol.png)

-Electronicsinfos.png)
.png)


0 Comments
please do not insert spam links