what are SF6 circuit breakers?
SF6 circuit breakers are a type of circuit breaker that uses sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas as the arc extinguishing and insulating medium. They are commonly used in high-voltage electrical power systems, including substations and power transmission networks.
SF6 circuit breakers are known for their excellent dielectric properties, high thermal conductivity, and efficient arc quenching capabilities.
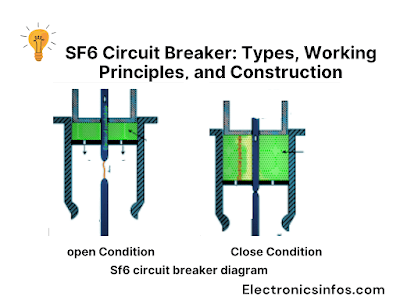
Sf6 circuit breaker diagram
Purpose Of SF6 circuit breaker
The main purpose of an SF6 circuit breaker is to interrupt the flow of electrical current in a circuit. when a fault or abnormal condition occurs, such as an overload or short circuit, the SF6 circuit breaker detects the fault current and initiates the opening of its contacts.
As the contacts open, a high-pressure SF6 gas is released into the interrupting chamber. The released gas creates a flow path for the fault arc and extinguishes it.
There are different designs available for interrupters including
Types of SF6 Circuit Breakers
- Single Interrupter SF6 Circuit Breaker
- Two Interrupter SF6 Circuit Breakers
- Three Interrupter SF6 Circuit Breakers
Single Interrupter SF6 Circuit Breaker
This type of circuit breaker consists of one interrupting unit in a single housing. It is commonly used for low-voltage applications.
In this design, two interrupting units are housed in a single enclosure. This type of circuit breaker is typically used for medium-voltage applications.
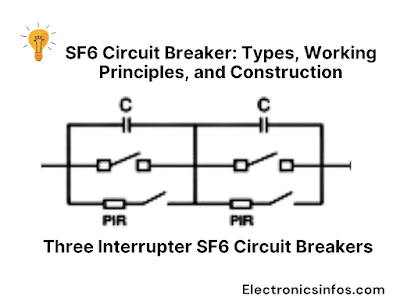
Three Interrupter SF6 Circuit Breakers
Three interrupting units are contained within a single enclosure in this type of circuit breaker. It is employed for high-voltage applications, typically in substations and power transmission systems.
Working Principles of SF6 Circuit Breaker
SF6 circuit breakers operate based on the principle of the self-blast technique. When a fault occurs, the high-pressure SF6 gas is rapidly released. The released gas creates a flow path for the arc and increases its length.
As the arc lengthens, the voltage across the contacts increases, and the current decreases to the point where the arc is extinguished. During normal operation, the circuit breaker contacts are closed, and the SF6 gas provides excellent insulation and extinguishing properties.
When a fault occurs, a control circuit detects the fault current and initiates the opening of the circuit breaker contacts.
Construction of SF6 Circuit Breaker
The construction of an SF6 circuit breaker involves several key components including
- Interrupting Unit
- Arc Interrupting Chamber
- Operating Mechanism
- Insulation
- Auxiliary Systems
Interrupting Unit of SF6 Circuit Breaker
The interrupting unit consists of Three contacts including
- Fixed Contact
- Moving Contact
- Arcing Contact
Fixed Contact
The fixed contact is a stationary part of the circuit breaker that remains in position during normal operation.
Moving Contact
The moving contact is connected to the operating mechanism and can be opened or closed as needed. It moves to create or break the electrical connection with the fixed contact.
Arcing Contact
The arcing contact is designed to withstand and control the arc generated during fault interruption. It helps to elongate the arc and facilitate effective arc quenching.
Arc Interrupting Chamber
- SF6 Gas
- Nozzle
- Arc Chutes
SF6 Gas
SF6 gas is used as the arc extinguishing and insulating medium within the arc interrupting chamber. It is stored in a high-pressure reservoir and circulated through the circuit breaker during operation.
Nozzle
The nozzle directs the flow of SF6 gas towards the arc. it enhances the cooling and elongation of the arc.
Arc Chutes
The arc chutes are designed to provide a controlled path for the fault arc. They help to cool and deionize the arc.
Operating Mechanism
- Manual / Motor Mechanism
- Spring Mechanism
Manual/Motor Mechanism
The operating mechanism controls the opening and closing of the circuit breaker contacts. It can be manually operated or motor-driven.
Spring Mechanism
A spring mechanism provides the required force for closing the contacts. it stores energy for the opening operation. The spring mechanism helps to ensure a quick and efficient response during fault conditions.
Insulation
Insulating Materials
Various insulating materials, such as epoxy or porcelain, provide insulation. These materials help to maintain the necessary electrical clearances and prevent flashovers or electrical leakage.
Auxiliary Systems
Control and Protection System
SF6 circuit breakers are equipped with a control and protection system. It monitors various parameters, such as fault currents, operating voltage, and temperature. This system helps detect faults and ensure the circuit breaker's proper functioning.
Gas Monitoring System
some circuit breakers use a gas monitoring system. It continuously monitors the gas pressure and quality. it allows for timely maintenance and gas refilling.
Advantages of SF6 Circuit Breakers
- High dielectric strength
- Rapid arc extinguishing
- Low maintenance required
- Long service life
- chemically stable
- non-toxic
- non-flammable
Sf6 circuit breaker ratings
Rated Voltage
SF6 circuit breakers are rated for voltage levels, such as 72.5 kV, 145 kV, 245 kV, 420 kV etc.
Rated Current
The rated current of an SF6 circuit breaker is 630 A, 1250 A, 2000 A, and higher
Conclusion
SF6 circuit breakers are vital components in electrical power systems. Understanding the types, working principles, and construction of SF6 circuit breakers helps select and operate these devices.
As technology advances, SF6 circuit breakers continue to be essential in maintaining electrical infrastructure's safety and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is an SF6 Circuit Breaker?
An SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride) circuit breaker is a type of circuit breaker that uses SF6 gas to extinguish the arc.
What are the types of SF6 Circuit Breakers?
There are mainly three types of SF6 circuit breakers
- Single Interrupter SF6 Circuit Breaker
- Double Interrupter SF6 Circuit Breaker
- Four Interrupter SF6 Circuit Breaker
How is SF6 gas managed in SF6 Circuit Breakers?
SF6 gas is managed through a closed loop including gas filling, compression, storage, and re-circulation.
What is the construction of an SF6 Circuit Breaker?
The construction of an SF6 circuit breaker includes:
- Interrupter Unit
- Operating Mechanism
- Gas System
- Control System
Also, Read on Electronicsinfos!





-Electronicsinfos.png)



0 Comments
please do not insert spam links