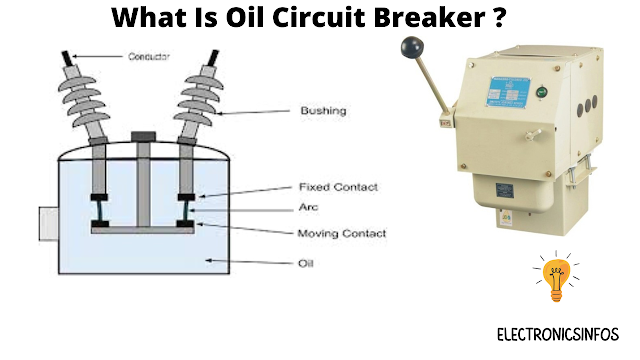
What is an Oil Circuit Breaker?
An oil Circuit breaker is a type of breaker in which Oil is used as a medium to provide insulation. we discuss two types of oil circuit breakers regarding oil filling including
Classification Of Circuit Breaker
- Bulk Oil circuit breaker
- Low Oil circuit breaker
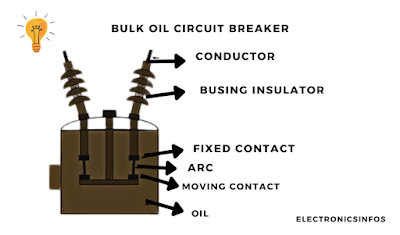
Bulk Oil circuit breaker
A bulk oil circuit breaker is a type of circuit breaker where all operating mechanisms and breaker contacts are immersed in a large quantity of oil. This oil serves a dual purpose: when the contacts are open, it not only provides insulation to the current-carrying parts but also acts as a medium for interrupting the arc during the breaking process.
 |
| Bulk Oil Circuit Breaker |
When the contacts of the breaker open, an arc is generated between them. The heat produced by the arc decomposes the oil into gases and vapours. As a consequence, the original oil is transformed into vaporized oil.
This vaporized oil replaces the space where the arc was, halting the arc-extinguishing process. During this transition to the vapour state, various reactions and actions take place within the oil. This process helps in extinguishing the arc.
Different parts of the oil circuit breaker Including
- Tank (Boiler Plates)
- Dielectric oil
- Moving Contacts (Copper)
- The gas formed by the decomposition of 2 (Hydrogen 70%)
- Arc Control Device
- Fixed Contacts
- Tension Rods
- Conductor Copper
- Bushing Oil filled
- Conductor
There are some limitations of the bulk oil circuit breaker is
- More oil quantity is used in the steel tank.
- The Dielectric strength is reduced over time.
- The tank size is large
Types of bulk Oil C.B W.r.t Construction
Different types of circuit breaker W.r.t Construction including
- Plain break Type O.C.B
- Self-Generated Pressure Type O.C.B
- Externally Generated Pressure Type O.C.B
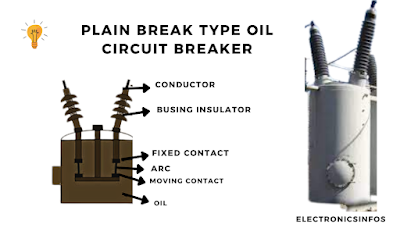
Plain breaks Type O.C.B
A plain break-type circuit breaker consists of a weather-tight steel tank that protects the circuit breaker from the environment. we fill a mineral oil in the tank. The fixed and moving contacts are immersed in the oil. when fixed contact is separate from moving contacts the arc is produced in between them.
The heat is produced due to the arc that temperature is reached up to 5000k. This high value of heat affects the oil and vaporizes it. there are different gasses produced i.e hydrogen, Methane Ethylene etc. These gasses also act as Explosives so The upper part of the tank is a strong sheet.
 |
| plain break Oil Circuit Breaker |
In normal conditions the fixed contacts and moving contacts are close. when faults occur the moving contacts are separate and the arc is produced between them which changes the oil into hydrogen gas. when contacts are separated the arc length is increased and the change in the ratio of oil to gas is decreased.
There are technical problems that occur in the O.C.B. due to gap length so this breaker is not used to handle the high current. This breaker is limited to 150 MVA. Two types of plain circuit breakers including
- Single break oil C.B
- Double Break Oil C.B
Single break oil C.B
Single Break CB is a type of plain oil circuit breaker where the arc is produced on a single bushing side.
Double Break Oil C.B
A double break oil breaker is a plain oil CB where two arcs are produced on two sides is called double break oil There are some limitations to a plain oil circuit breaker including
Self-Generated Pressure Type O.C.B
A Self-Generated Pressure Type Oil Circuit Breaker (O.C.B.) is a specific type of oil circuit breaker that operates based on the pressure generated within the breaker itself during a fault condition.
It consists of a chamber filled with insulating oil, contacts for interrupting the circuit, and mechanisms for generating pressure within the chamber.
Externally Generated Pressure Type O.C.B
An Externally Generated Pressure Type Oil Circuit Breaker (O.C.B.) is a type of oil circuit breaker that relies on external mechanisms to generate pressure within the breaker chamber during a fault condition.
It consists of a chamber filled with insulating oil, contacts for interrupting the circuit, and mechanisms for generating pressure externally, such as hydraulic or pneumatic systems.
Limitations of bulk Oil C.B
- This breaker is not used up to 150 MVA because of its high size.
- This breaker has a long and unreliable arching time.
- This breaker has no fast interruption.
Advantages of bulk Oil C.B
- The Arc distinguish time as fast.
- The Gasses which is produced in the oil also provide effective cooling.
- The Oil provides Good Dielectric properties.
- The Dielectric property minimizes the Arc Restriking.
- The construction of an oil circuit breaker is simple.
- Oil Circuit breakers have a high Rupturing capacity.
- Oil CB is Suitable for manual and Automatic Operations.
- There is space available in the busing to set the C.T.
Disadvantages of bulk Oil C.B
- The Chance of Explosives is Available because of Explosive Gasses produced in the medium.
- They need maintenance regularly.
- The operating cost is high.
- The Efficiency is Affected due to gasses produced in the Tank.
- The Tank size and weight are large.
- We need Regular checkups to maintain the oil quality and quantity.
- We need expensive heavy mineral oil.
- This is not suitable for outdoor purposes.
- The Wear and tear of contacts are possible.
- We need a high quantity of steel.
Minimum Oil circuit breaker
A Minimum-oil circuit breaker is a type of oil circuit breaker in which the minimum or small quantity of oil is used in the tank. The current-carrying parts are insulated with porcelain or any other insulating medium. In the Bulk Oil Circuit breaker, the 10% oil is just used to distinguish the arc.
The remaining 90% is used to earth the live parts. There is a small container in the minimum oil CB to hold the Oil. The container is supported by a Porcelain insulator that provides enough insulation. Minimum Oil C.B. needs less space as compared to Bulk Oil C.B. There are different ranges of Minimum Oil CB available on the market.
Ranges of Minimum Oil C.B
- 3.6KV
- 7.2KV
- 12KV
- 36KV
- 72.5KV
- 145Kv
- 245KV
- 420KV
Construction Of Minimum oil C.B
Two compartments in the Minimum-oil C.B. are filled with Mineral Oil. The upper Chamber is called the circuit chamber and the lower chamber is called the supporting chamber.
These two chambers are separated from each other so oil is not entering another compartment. The Circuit Braking Chamber need a Low quantity of oil. The Circuit Braking Chamber consist of the following parts
- Upper and lower fixed contacts
- Moving Contacts
- Turbulator
Advantages Of Minimum Oil C.B
- Need a Low quantity of oil to distinguish the arc.
- The Size and weight are small.
- The cost is low.
- suitable for manual and automatic operations.
- The low oil breaker needs less space.
Disadvantages Of Minimum Oil C.B
- The Lifetime of contacts is small
- The Chance of Explosion is available.
- They need regular maintenance.
- Restocking Action is possible.
- They faced a problem carrying the C.T.
- We need regular oil level checkups.
- The degree of carbonization is high.
Applications Of Oil Circuit Breaker
- OCBs are used to protect high-voltage power grids, ensuring safe operation and maintenance.
- They are installed in substations to control the flow of electricity and protect the network from faults.
- OCBs are employed in power transmission systems to interrupt overcurrents and short circuits, preventing damage to the infrastructure.
- They serve a crucial role in distribution systems, safeguarding electrical components from fault conditions.
- OCBs find applications in industrial settings, where they protect equipment from electrical surges and faults.
- They are used in systems with voltage ratings up to 220 kV for controlling and maintaining stable voltage levels.
Conclusions
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is an Oil Circuit Breaker (OCB)?
How does an OCB work?
What are the types of OCB?
- Bulk Oil Circuit Breaker (BOCB), which uses a large quantity of oil,
- Minimum Oil Circuit Breaker (MOCB), which uses a smaller amount of oil


.png)
-Electronicsinfos.png)

0 Comments
please do not insert spam links