What is a Transformer?
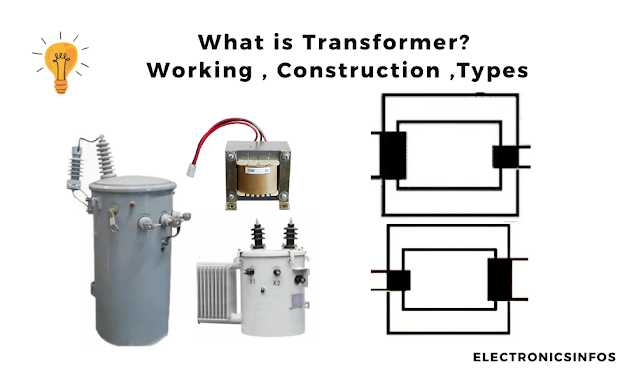 |
| What is a Transformer? |
input voltage/output voltage =N1/N2 =K
K = Turn Ratio
Electromagnetic Induction
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction is a fundamental principle in physics that describes how a changing magnetic field can induce an electromotive force (EMF). The induced electromotive force (EMF) in any closed circuit is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit.
Faraday’s laws of Electromagnetic Induction as
e= -N*dφ/dt
The negative sign in Faraday's law indicates the direction of the induced current (and thus the induced EMF) according to Lenz's Law.
 |
| circuit diagram of a transformer |
EMF Equation Of transformer
The Emf Equation of an electrical transformer is a Mathematical Expression that defines the relationship of Primary Induced voltages to Secondary Induced voltages.
K=N2N1
- K>1 For Step Up Transformer
- K<1 For Step-Down Transformer
 |
| EMF Equation of transformer |
Construction of Basic transformer
The construction of a basic transformer involves several components that work together to transfer electrical energy between two or more coils. The basic components including
- Core
- Primary Coil
- Secondary Coil
- Insulation
Types of transformer w.r.t core
There are two types of transformer w.r.t core including
- Core-type Transformer
- Shell Type Transformer
Core type Transformer
A core-type transformer is one where the windings are wound around the core, creating a single path for the magnetic field. This design minimizes magnetic leakage.Smaller core-type transformers are built with rectangular or cylindrical forms, while larger ones use circular or cylindrical coils. it is less expensive compared to
the shell type.
the shell type.
Shell type Transformer
A shell-type transformer has two paths for the magnetic field. The core surrounds the windings, which are inside. The coils are wound in layers, like a stack of discs, and insulated with paper. Shell-type transformers can be rectangular or distributed in shapes. we do not prefer natural cooling in the shell-type transformer. Shell-type transformer maintenance is difficult because both coils are on the same limb.Types of transformer w.r.t voltage
- Step-up Transformer
- Step-down Transformer
Step-up Transformer
A Step-Up Transformer is a transformer in which the primary voltage is lower than its Secondary voltage. The primary windings are less than the secondary windings in step down transformer.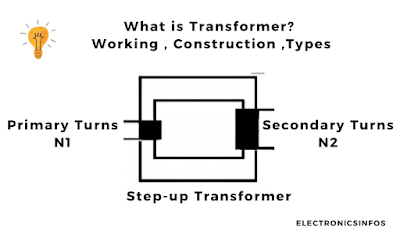 |
| Step-up Transformer |
Step down Transformer
A Step-Down Transformer is a distribution transformer in which the secondary voltages are lower than its primary voltage. The primary windings are more than the secondary windings in step-down transformers.Types of transformer w.r.t Phase
- Single Phase Transformer
- Three-phase Transformer
Single Phase Transformer
A single-phase transformer is a type of transformer which operates in a single-phase supply. It's a passive electrical device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. In a single-phase transformer, there is one primary and one secondary winding.Three-Phase Transformer
In a three-phase transformer, there are three primary and three secondary windings. The Basic Principle of the three-phase transformer is Electromagnetic induction. three-phase transformer is an important part of the transmission system.The three-phase transformer has two yokes and three limbs to support the winding structure of the transformer. In a three-phase transformer, the angle between each winding is 120 degrees electrical. Three-phase transformers are commonly used for generation, transmission and distribution purposes.
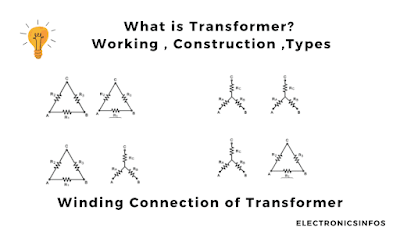
There are different connections of windings including
- Star-Star Connection
- Star -Delta Connection
- Delta -Delta Connection
- Delta-star Connection
Types of Transformer W.r.t cooling
- Oil-immersed self cold
- A combination of oil-immersed and air-blast
- Oil-immersed water cold
- Oil-immersed forced oil cold
- A combination of oil-immersed self-cold and water-cold
- Oil-forced, air-forced cold
- Forced oil-water cold
- Forced oil self-cold
Core Material
The core material of a transformer plays an important role in its performance and efficiency. It provides a low reluctance path to the magnetic fields. The two main types of materials used for transformer cores are
- Iron (or Ferromagnetic Alloys
- Ferrites
Iron (or Ferromagnetic Alloys
Iron and its alloys have high magnetic permeability, allowing them to efficiently conduct magnetic flux. Silicon steel is widely used due to its low core loss and high magnetic permeability. The iron core is suitable for power transformers. Silicon steel is also known as electrical steel.
Ferrites
Ferrites are ceramic materials with magnetic properties. They are used in applications requiring high-frequency operation, such as electronic transformers and radio-frequency devices. Ferrites have lower magnetic permeability. Manganese-zinc ferrite and nickel-zinc ferrite are examples of Ferrites.
Which Factors Consider When Selecting Core Material?
- Magnetic Permeability Must Be high which contributes to the transformer's performance.
- eddy current and hysteresis losses must be lower in Core materials leading to higher transformer efficiency.
- Materials with higher saturation flux density are advantageous for transformers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Without transformers, the landscape of power generation, transmission, and distribution would be vastly different, and much less efficient transformers, in particular, step-up transformers play a crucial role in increasing voltage levels to minimize energy loss during transmission.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does a transformer work?
Transformers operate on the principle of mutual induction and can either increase or decrease the AC voltage in an electrical circuit.
What are the main parts of a transformer?
The main components include a laminated iron core and two coils of wire, known as the primary and secondary windings.
What are the different types of transformers?
Common types include step-up, step-down, isolation, single-phase and three-phase transformers,
What are transformers used for?
They are essential in transmitting and distributing electrical power and adjusting voltage levels.
Related Posts
3 Types of Electrical Transformers w.r.t Core
Regulations of Electrical Transformer?
single-phase vs three-phase transformers.




-Electronicsinfos.png)



0 Comments
please do not insert spam links