What is a Current Transformer?
A Current Transformer (CT) is an instrument transformer used to measure alternating current (AC) in electrical systems. It consists of a primary winding, which carries the current to be measured, and a secondary winding which generates a proportionally reduced current.
Burden Vs Saturation
Current transformers (CTs) are used to measure the electrical currents which provide accurate secondary current output. In this article, we discuss the Burden, Saturation and curve of transformer saturation.
Burden of CT(Current Transformer)
The burden of a current transformer is the impedance to its secondary winding. A Burden is also defined as the total secondary resistance of the current transformer. Total resistance combines secondary winding resistance and leads and relay resistance. The burden is expressed in ohms or volt-amperes (VA).A Maximum Burden of C.T Depending on the Turn Ratio, the Current rating of C.T
What is the effect of Burden on CT (current Transformer)?
The burden affects the performance of the CT and its accuracy. When a CT is connected to a load, a voltage drop across the secondary impedance is created due to the secondary current flowing through it.
This voltage drop can introduce errors in the secondary current measurement, mainly if the burden impedance is not within the specified limits of the CT.
It is important to ensure that the burden impedance is within the acceptable range specified by the CT manufacturer. If the burden impedance is too low, it can result in excessive secondary current and potentially cause CT saturation.
On the other hand, if the burden impedance is too high, it can cause excessive voltage drop and result in inaccurate measurements.
Burden Calculation of Current Transformer
Let's consider a current transformer with the following details
- Primary Current Rating (Ip): 1000A
- Turns Ratio (N): 1000:5 (Primary: Secondary)
- Burden (B): 5 VA (Volt-Amps)
The burden of a CT is calculated using the formula
where
- (Is) is the secondary current in amps.
- (Vs) is the secondary voltage in volts.
Using the turns ratio, we can find the secondary current
Substituting the values into the burden formula
Therefore, if the secondary current is 1A, the secondary voltage ( Vs ) required to achieve a 5 VA burden is 5000 volts.
Cautions
Properly matching the burden impedance to the CT's specifications is crucial for accurate current measurement. It ensures the CT operates within its optimal range and minimizes errors caused by burden-induced voltage drops.
Burden ratings for IEC CTs
- 1.5 VA
- 3 VA
- 5 VA
- 10 VA
- 15 VA
- 20 VA
- 30 VA
- 45 VA
- 60 VA
The burden rating of ANSI/IEEE C.T
- B-0.1
- B-0.2
- B-0.5
- B-1.0
- B-2.0
- B-4.0
Saturation of Current Transformer(C.T)
Saturation is a phenomenon that occurs when the primary current of a current transformer exceeds its rated limit which causes distortion in the secondary current waveform. Saturation occurs when the magnetic core of the CT reaches its magnetic saturation point.
When a CT is saturated, its core is unable to magnetically amplify the primary current accurately, leading to distorted secondary current readings. Saturation can occur due to high fault currents, transient overloads, or improper selection of CTs for the specific application.
What is the effect of saturation on CT(current transformer)?
When a CT becomes saturated, its core cannot amplify the primary current accurately, resulting in distorted secondary current readings. Saturation can be triggered by high fault currents, transient overloads, or improper selection of CTs. Saturation affects the accuracy and performance of the CT.
Transformer saturation Curve of Current Transformer
Saturation Calculation of Current Transformer
Saturation in a CT occurs when the core becomes magnetically saturated due to excessive primary current, leading to inaccurate readings.
Suppose we have a CT with the following details
- Saturation Current (Isat): 1200A (maximum current before saturation)
- Primary Current Rating (Ip): 1000A
- Turns Ratio (N): 1000:5 (Primary: Secondary)
To calculate the primary current that would cause saturation, we use the turns ratio
Using the turns ratio to find the corresponding primary current
Therefore, when the primary current reaches 1200A, the CT will saturate and may no longer provide accurate measurements.
How to find Current Transformer Performance Calculation?
Let's work through an example to calculate the performance of a current transformer (CT) using the provided parameters
Step-1 : Assumptions
- Turns Ratio (N): 1000:5 (Primary: Secondary)
- Rated Primary Current (Ip): 1000A
- Burden (B): 5 VA
- Saturation Current (Isat): 1200A
- Accuracy Class: Class 1
Step-2: Turns Ratio Calculation
The turns ratio ( N ) is given as 1000:5. For every 1000 amps on the primary side, the CT produces 5 amps on the secondary side. Therefore,
Step-3: Rated Secondary Current (Is)
Since ( N = 200 ), the rated secondary current ( Is ) is calculated as
Step-4: Burden Calculation
The burden ( B ) is given as 5 VA. This represents the maximum load impedance the CT can handle without affecting accuracy. The burden formula is
where
- ( Is ) is the secondary current and
- ( Vs ) is the secondary voltage.
Substituting the values, we get
Solving for ( Vs ), we find ( Vs = 1000V ).
Step-5: Accuracy Calculation
The accuracy class is Class 1, which means the CT provides an accuracy of ±1%. For a rated secondary current of 5A, the accuracy can be calculated as
Step-6: Saturation Analysis
The saturation current ( Isat ) is given as 1200A. This represents the maximum primary current before the CT becomes saturated.
In our case, the rated primary current ( Ip ) is 1000A, below the saturation current. Therefore, the CT will not saturate under normal operating conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the burden of a current transformer?
How is the burden measured?
Why is the burden important for CT operation?
What are the burdens for different applications?
How can I calculate the total burden on a CT?
What is saturation in a current transformer?
What causes a CT to saturate?
How can I prevent CT saturation?
Also, Read on Electronicsinfos!
What is a Current Transformer?
Accuracy Class Of Current Transformer
How to Reduce The Transformer Losses?
Single Phase Transformer Vs Three Phase Transformer
EMF Equation Of Electrical Transformer

-Electronicsinfos.png)





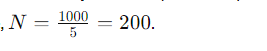



-Electronicsinfos.png)



0 Comments
please do not insert spam links