What is the Parallel Operation Of a Single-Phase Transformer?
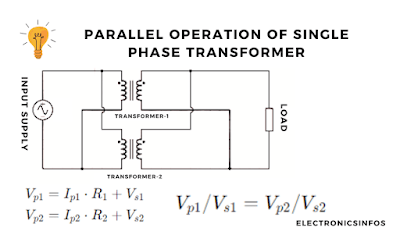
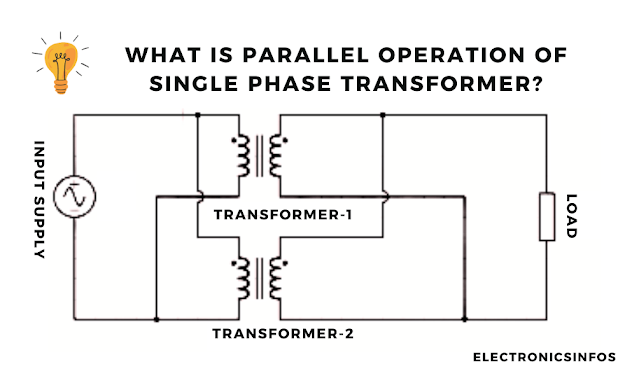
When the primary winding of Two or more single-phase transformers is connected with a common input supply or bus bar is called the parallel operation of a single-phase transformer.
The primary windings are connected to the supply busbar and the Secondary windings are connected to the load busbar.
Need For Parallel Operation
Sometimes on the transmission and distribution side, The load capacity is high and the transformer still needs to fulfill the requirements of the load. Now there are two ways: we used a Single higher capacity transformer or the same capacity of a different transformer in parallel.
The best option is to operate more than one transformer in parallel to fulfil the load requirements.
- Multiple Transformer provides a Backup option in case of Maintenance is needed.
- Parallel operation provides uninterruptable supply to the load.
- Parallel operation enhances the stability of the system.
- Parallel operation is economically feasible.
 | |
|
parallel equation of single-phase transformer
- Vp1 and Vp2 are the primary voltages of the transformers.
- Vs1 and Vs2 are the secondary voltages of the transformers.
- Ip1 and Ip2 are the primary currents of the transformers.
- Is1 and Is2 are the secondary currents of the transformers.
Conditions for Parallel Operations
- Polarity Must be the same (Necessary Condition)
- Turn Ratio(Necessary Condition)
- Frequency and voltage
- Same Equivalent Resistance and reactance (X/R Ratio)
Polarity
Both transformer polarities must be the same otherwise short circuit operation happens.
Frequency and voltage
The transformer's primary windings are designed according to the supply system voltages and frequency.
Transformation Ratio
The turn ratio must be Identical to operate the transformer in parallel.
Same Equivalent Resistance and reactance
The value of resistance and reactance of winding must be the same to operate the transformer in parallel. In Simple words X/R ratio must be the same.
Advantages of Parallel Operations
- If we operate the transformer in parallel the cost is minimized as compared to the single large unit.
- The reliability factors are high in parallel operations of the transformer as compared to the single large unit.
- The management of a parallel transformer unit is easy.
- The overall capacity of the system is increased.
- Easy to add and remove the transformer as per load requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the parallel operation of single-phase transformers is a critical aspect of electrical engineering. when transformers are connected in parallel, they share the load proportionally to their ratings.
However, it is essential to ensure that the transformers are properly matched in terms of voltage, phase sequence, and impedance.
FAQS(Frequently Ask Questions)
What conditions must be met for the parallel operation of single-phase transformers?
- Transformers must have the same voltage rating and frequency.
- Their phase sequence must match.
- They should have the same turn ratio.
How do voltage ratios affect the parallel operation of transformers?
Why is it important to match the polarity of transformers in parallel?
Matching polarity ensures that the voltages of the transformers add up in the correct phase. If polarity is not matched, the voltages could cancel each other out or add up in undesirable ways, leading to inefficient operation.Can transformers with different kVA ratings be operated in parallel?
Transformers with different kVA ratings can be operated in parallel, but load sharing will be proportional to their ratings. Transformers with higher kVA ratings will carry more load than those with lower ratings.
What are the advantages of operating transformers in parallel?
- Enhanced reliability of transformers to share the load.
- Flexibility in managing loads without disrupting the entire system.
- Improved efficiency by utilizing the capacity of multiple transformers efficiently.
How does the per-unit leakage impedance relate to parallel transformer operation?
Per unit leakage impedance helps determine how much current a transformer will draw for a given voltage. In parallel operation, transformers with similar per-unit leakage impedances will share the load more evenly.
What could happen if transformers in parallel have different secondary voltages?
If transformers in parallel have different secondary voltages, they won't share the load evenly. This can lead to imbalances and overheating of some transformers.Related Posts
How to Reduce The Transformer Losses?
Single Phase Transformer Vs Three Phase Transformer
EMF Equation Of Electrical Transformer

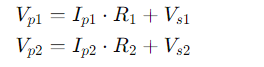
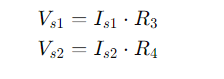


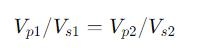

-Electronicsinfos.png)



0 Comments
please do not insert spam links