Testing Method Of Electrical Power Transformer
- Mechanical Test
- Electrical Test
- Routine Test
- Type Test
Routine Test
There are many types of Routine Tests including
- Ratio And Polarity
- Load Loss
- Impedance
- Insulation Resistance
- Resistance of Windings
- No-load Loss
- No-Load Test
- Voltage Test windings
- Core insulation Voltage test
Type Test
- Temperature Rise Test
- Impulse Voltage Test
- Noise Level Test
- Polarity Test
- Open Circuit Test
- short circuit test
- Ratio Test
- Insulation Test
- Back-Back test
Polarity Test
The Polarity of a transformer is the Direction of Current flowing in each terminal. Some standards show When you Stay on the high voltage side of the transformer, mark H1 on one side and H2 on the other side.
There are two types of connection available W.r.t polarity, one is Additive and another is Subtractive. Additive polarity means both voltages are added and subtractive polarity means both voltages subtract each other.
How to check the polarity of a single-phase transformer?
To check the Accurate polarity of a single-phase transformer we need a Standard Transformer that Polarity is Known and another transformer whose polarity needs to be determined is available for the same ratio and voltage.
Procedure of polarity test
- Connect H.T Leads and L.T Leads in parallel to each other.
- Connect the Fuse on the Secondary Side of the Transformer.
- If Both transformers have the same polarity There is no current flowing in L.T Leads.
- If Both transformers are in opposite polarity the L.T. windings are Short circuits and the fuse is cut off the Circuit.
Note: Fuse Ratings Must Be low Value.
Additive Polarity
Subtractive Polarity
Check the polarity with the help of Voltmeter
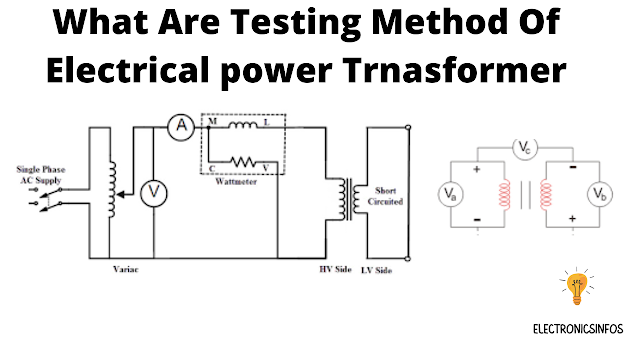
Open Circuit Test
The Open Circuit Test is Also called the No load test. The purpose of this test is to calculate the no-load loss and no-load current. To perform this test we use one winding of the transformer especially prefer high voltage winding.
Procedure of open circuit test
- open high voltage winding of the transformer.
- connect Low voltage winding with normal supply voltage.
- connect the watt meter, ampere meter and volt meter with low voltage winding.
When we apply normal voltage to the primary winding the normal flux is produced in this winding and iron losses appear across the watt meter.
There are no Copper losses that occur because the circuit is open. when we connect the voltmeter in the secondary circuit it shows induced EMF so we can easily find the Transformation Ratio K.if watt meter reading is known we can easily find the following values
Formulas
Short circuit Test
The Short circuit test is also called the Impedance Test. This test is conducted to find the
- Equivalent Impedance (Z01 or Z02)
- Leakage Reactance(X01 or X02)
- Total Resistance(R01 or R02)
- Full-load copper loss
- Total voltage Drop
- To find The regulation of the transformer
Procedure of short circuit test
- Short The low winding with a heavy Conductor to Find the Rated load current.
- Connect the primary winding with Normal frequency and Voltage and increase this voltage step by step to flow the full load current in primary and secondary windings.
- In this method, The induced Mutual flux is X percentage of the Main Flux.
- The Core loss is very low so the Watt meter shows purely full-load copper loss.
- Z01=Vsc/I1
- W=I2R01
- X01=√Z01² - R01²
Ratio Test
There are two methods to perform the Ratio Test, which test is chosen depending on the availability of Equipment. The Most used Method 1 is
Method 1
we provide a Specific Voltage to the High-voltage winding of the transformer and measure the other winding voltage with the help of a volt meter or Potential Transformer.
Record the Different Ratios on different turns of windings and compare them.
Method 2
- In This Method, We Compare under test meter with a calibrated standard Meter.
- Standard Meter divided into small Turns Ratio.
- Connect the Standard Transformer and Under test transformer in Parallel.
- Energise the high voltage windings of Both transformers.
- The low-voltage winding of the transformer is connected to a Sensitive Amp Meter.
- Check the under-test transformer ratio w.r.t standard transformer and record their values.
Ratio Test With The Help of Ratio Meter Transformer
- The under-test transformer high voltage winding is connected with a low voltage main supply of 220 or 400 volts.
- Compare the induced voltage on the secondary with the Ratio meter output voltage.
- Connect the ampere meter on both windings.
- regulate the transformer tapings till the ampere meter shows 0 amperes.
- When the ampere meter shows 0 amperes it means both transformer ratios are equal and their voltages are also equal.
- Now you can easily find the values with the help of a standard meter.
Insulation Test
if a transformer is working under normal operating conditions and if we apply high voltage for a Specific Time to check its insulation or dielectric strength is called an insulation test.
To check the insulation of the power transformer we conduct the following high-voltage tests
- Power Frequency Voltage test
- Impulse Voltage testing
Power Frequency Voltage test
power frequency voltage test is categorised in type and Routine Test. In this test, we provide a high voltage value for specific times. This high voltage does not break the insulation otherwise this test is considered to fail. The test voltage depends on the type of transformer(Dry or Oil).
Impulse voltage is categorised in the Type test. we provide a standard impulse wave of 1.2/50us of one winding. The other winding, tank and core are earthed. The purpose of this test is to find the faults due to the Switching, Lightning etc
Back-to-Back test
A back-to-back test is used to find the Temperature developed under load conditions. Back to back test is also called the sumpner Test. The limitation of this test is we need two same transformers.
Procedure
In this test, we connected two transformers in parallel and applied normal voltage and frequency. The secondary winding is connected in series and their Phase in opposite directions.
We use a voltage regulator on the secondary side and change the voltage gradually To measure the total iron losses and copper losses with the help of watt meters.
When Switch s is open watt meter W1 measures core losses. We Connect secondary winding in such a way it has potential in the opposite direction, this is only possible when Vab=Vcd So watt meter W2 Measure the copper loss.
Type Test
Type tests in transformers are conducted on a particular type of transformer. These tests are performed to evaluate the performance characteristics of the transformer.
Type tests are essential to ensure that transformers meet industry standards and regulatory requirements. There are different types of type tests including
Temperature Rise Test
The Temperature Rise Test is designed to ensure that a transformer can operate within specified temperature limits under normal load conditions. This test is not only a measure of the transformer's ability to handle electrical stress but also a predictor of its longevity and reliability.
Procedure of Temperature rise test
- Short-circuit the Low Voltage (LV) winding of the transformer.
- Apply a voltage to the High Voltage (HV) winding to induce the rated current.
- Measure the power input to account for no-load losses and load losses, adjusted to a reference temperature, typically 75°C.
- Place thermometers in strategic locations, such as the top oil pocket and at the inlet and outlet of the cooler bank.
- Record hourly temperature readings of the top oil and the ambient temperature around the transformer.
- Continue the test until the top oil temperature reaches a steady state, which is when the temperature rise is less than 3°C in one hour or does not vary more than 1°C per hour for four consecutive hours.
Note :
Impulse Voltage Test
Test Procedure
- Application of a reduced impulse voltage, typically 75% of the transformer's Basic Impulse Level (BIL), to check for preliminary insulation performance.
- A full-wave impulse at 100% BIL is then applied to assess the insulation under standard conditions.
- Chopped-wave impulses at 100% BIL follow, to test the insulation's response to abrupt voltage changes.
- Finally, additional full-wave impulses at 100% and 75% BIL are applied to complete the assessment.
Noise Level Test
The noise level test in transformers is conducted to measure the sound produced by the transformer during operation. Excessive noise can be a sign of mechanical issues or inefficient design.
Transformer noise is primarily caused by a phenomenon known as magnetostriction. When the magnetic core of a transformer is magnetized, it experiences minute changes in dimension.
This effect is cyclical with the alternating current, causing the core to expand and contract, generating sound waves that propagate through the surrounding structures and air.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the testing of electrical power transformers is a critical process that ensures their reliability and safety in operation. Through a series of routine and special tests, manufacturers can verify that transformers meet the required specifications and performance standards.
Faqs(Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the Temperature Rise Test in a transformer, and why is it important?
What is the Dielectric Strength Test, and how does it assess transformer insulation?
Why is the Short-Circuit Test conducted on transformers?
What is the purpose of the Impulse Voltage Test in transformer testing?
What is the purpose of the Insulation Resistance Test in transformer testing?
Related Posts :
How to Reduce The Transformer Losses?
Single Phase Transformer Vs Three Phase
Transformer
EMF Equation Of Electrical Transformer








.png)
.png)

-Electronicsinfos.png)
.png)

0 Comments
please do not insert spam links