Comparison Between Electrical Relays And Circuit Breakers
 | |
|
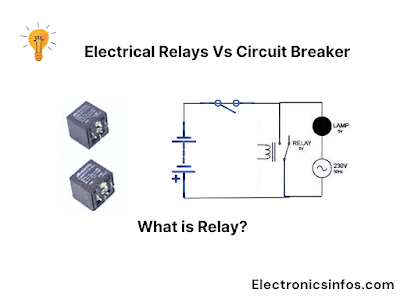
What is Relay?
A relay is an electrically operated switch that is used to control the flow of electricity in a circuit. It consists of an electromagnet (coil) that, when energized, generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field causes a set of contacts to either open or close the electrical circuit.
 |
| Electrical Relay vs Circuit Breaker |
Types of Relays
- Electromechanical Relays
- Solid-State Relays (SSRs)
- Thermal Relays (Overload Relays)
- Protective Relays
- Latching Relays
- Reed Relays
Electromechanical Relays
- SPST (Single-Pole Single-Throw) Relay
- SPDT (Single-Pole Double-Throw) Relay
- DPST (Double-Pole Single-Throw) Relay
- DPDT (Double-Pole Double-Throw) Relay
Solid-State Relays (SSRs)
- Zero-Crossing SSR
- Random-Crossing SSR
Relays
- Relays are electromechanical switches that use an electromagnet to control the opening and closing of one or multiple switch contacts.
- They are used to control high-power or high-voltage circuits using a low-power signal.
- Relays do not usually require resetting after the operation, as they return to their original state once the control signal is removed.
- Relays generally have slower response times compared to circuit breakers.
- Relays typically have lower current ratings and are used for controlling smaller loads,
- Relays are used for controlling the flow of electric current in a circuit.
- Relays are used in applications where there is a need for electrical isolation between the control circuit and the controlled circuit.
- They are used for various purposes, such as controlling motors, switching high-power loads, or providing galvanic isolation.
- Relays are primarily used for control purposes, such as switching electrical devices, amplifying signals, or providing time delay functions.
- Relays operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction,
- Relays do not have built-in fault detection capabilities.
- Relays do not have a tripping mechanism, as they do not provide protection against overcurrent events.
- Relays can handle a wide range of voltages, depending on their design and ratings.
- Relays are generally less expensive compared to circuit breakers.
- Relays can control different types of electrical loads, including resistive, inductive, and capacitive loads.
- Relays do not dissipate energy during operation.
- Relays have a longer lifespan.
- Relays do not provide arc suppression capabilities.
- Relays are generally compact and come in various sizes.
- Relays can be easily integrated into various control systems and circuits.
- Relays do not interrupt the circuit during normal operation.
- Relays act as a protective device that sends the signal to the circuit breaker.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is an electrical switching device that automatically interrupts or breaks an electric circuit when it detects excessive current or a fault in the electrical system.
 | |
|
Types of Circuit Breaker
- SF6 Circuit breaker(SF6)
- Air Circuit Breaker(ACB)
- Oil Circuit Breaker(OCB)
- Vacuum Circuit breaker(VCB)
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
- Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
- Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) or Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
- Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
- Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI)
- High Voltage Circuit Breaker
- Miniature Circuit Breaker with Overload Protection (MCBO)
Circuit Breakers
- Circuit breakers do not provide isolation but offer protection against overcurrent events.
- circuit breakers are used for protecting electrical circuits from overcurrent conditions
- Circuit breakers are primarily used for controlling and protecting resistive and inductive loads.
- Circuit breakers are designed to quickly interrupt the circuit upon detecting an overcurrent event.
- Circuit breakers can detect fault conditions such as short circuits, overloads, or ground faults.
- Circuit breakers are larger and bulkier due to their protective mechanisms and higher current ratings.
- circuit breakers have higher current ratings and can handle larger current levels.
- circuit breakers work on the principle of thermal or magnetic trip mechanisms.
- Circuit breakers are automatic switches designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent conditions.
- Circuit breakers dissipate energy in the form of heat when interrupting the current flow.
- Circuit breakers are designed to extinguish or suppress the arc that occurs during the interruption of the circuit.
- Circuit breakers have a built-in mechanism that trips and opens the circuit when an overcurrent condition occurs.
- They are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications to protect against short circuits, overloads, and ground faults.
- Circuit breakers are available in different types, such as thermal-magnetic, magnetic, and ground fault circuit breakers.
- Circuit breakers provide a faster response time compared to relays, as they are designed to quickly interrupt the circuit in case of an overcurrent event.
- Circuit breakers need to be manually or automatically reset after tripping to restore power to the circuit.
Related Posts
Surge Protectors Vs Power Strips
Electrical Safety Training Tips
5 Battery Backup Surge Protectors
5 Best Digital Temperature Sensors

-Electronicsinfos.png)

.png)

0 Comments
please do not insert spam links