What are AC Generators or Alternators?
AC generator or Alternator is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in the form of an Electrical current is called an AC generator or alternator.
It is used to generate electricity in power plants, vehicles, and other applications where a reliable source of electricity is needed.
The frequency and voltage of the generated AC current depends on the speed of the rotor and the number of poles in the generator.
AC generators are typically designed to produce a specific voltage and frequency and are often interconnected in parallel to provide a larger, more reliable source of electricity.
Basic Principle of Alternator or AC Generator
The Basic Principle of an Alternator or an AC generator is Electromagnetic Induction. When the rotor rotates, the stator conductors are cut by the magnetic flux hence they alternating induced emf in them.
An AC generator works by using a rotating magnetic field to induce an electrical current in a set of stationary coils, known as the stator. The magnetic field is created by rotating a set of magnets, known as the rotor, within the stator.
As the magnets rotate, they generate a changing magnetic field, which induces an alternating current in the stator coils. The frequency of induced emf depends on the Numbers of N and S poles and their direction is found using Fleming's right-hand Rule.
The Induced Emf Depend on
- number of armature coil turns = N,
- magnetic field strength= H,
- the speed of the rotating field =f
Ac generators consist of Armature windings and a Magnetic Field. the significant difference between DC generators is the field is rotated and the armature is in a stationary condition in the alternator and reversed in the DC generator.
In their case, armature windings are mounted on a stationary element called a stator and field winding is mounted on a rotating element called the rotor.
Parts Of Alternators or Ac Generators
- Field winding
- Armature
- Prime Mover
- Rotor
- Stator
- Slip Rings
Field Winding of AC Generator
There are two types of field located on the alternator one is the field winding whose purpose is to produce the Magnetic Flux and the type of winding is Damper winding which is used to prevent the hunting(Speed Fluctuations) in generators.
Armature of AC Generator
The part of the Alternator or AC generator where EMF is produced is called an armature.
prime mover of AC Generator
The prime mover is the part of the alternator.it is used to drive and regulate the AC generators. The prime mover is either a steam turbine, diesel engine or motor to regulate the AC generator.
Stator of AC Generator
The stator consists of a cast iron frame which supports the armature core. The slots on the armature are the inner periphery for housing the armature conductors. The rotor is like a flywheel having alternate N and S poles fixed to its outer rim.
The magnetic poles are excited with a DC current of magnitude 125 to 600V. The core is laminated to minimize loss due to eddy currents. The laminations are insulated from each other and allow the cooling to pass through them.
Rotor of AC Generator
There are two types of rotor used in alternators
- Salient Pole type
- Smooth Cylindrical Type
Salient-type Rotor
Salient pole-type rotor used in low and medium-speed alternators. Such generators are characterised by their short axial length and large diameters. The pole and pole shoes are laminated to minimize heating due to eddy currents.
Smooth Cylindrical Type Rotor
A smooth cylindrical type rotor is used for high-speed alternators. These types of generators are designed for 2-pole and 4-pole. The rotor consists of smooth solid forged steel cylinders.
Slip Rings
A slip Ring is a part of an AC generator.it is used to conduct the flow of current from a stationary device to a rotating one.
EMF equation of an AC generator
Faraday's law states that the induced emf 'e' in a coil is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux ф through the coil. Mathematically, it is expressed as
Magnetic Flux ф
Magnetic flux is the product of the magnetic field 'B', the area 'A' perpendicular to the field, and the cosine of the angle theta 'θ' between the field and the normal the area. For a rotating coil in a magnetic field, the flux is given by
Consider a coil with 'N' turns, rotating in a uniform magnetic field 'B' with an angular velocity omega 'ω'. The area 'A' of the coil is constant.
As the coil rotates, the angle 'θ' between the magnetic field and the normal to the coil changes with time. If the coil starts from a position where the normal to the coil is parallel to the magnetic field, then
- where 't' is the time and
- 'ω' is the angular velocity.
The induced emf 'e' is the negative rate of change of magnetic flux. Therefore
Differentiating the flux for time 't'
Since the coil has 'N' turns, the total induced emf 'E' is
Thus, the instantaneous emf 'E' can be written as
where
- E_max = N . B. A .ω ) is the maximum induced emf.
- N is the number of turns in the coil.
- B is the magnetic flux density.
- A is the area of the coil.
- ω is the angular velocity of the coil.
- t is the time.
This is the EMF equation for an AC generator.
Advantages Of Stationary Armature
The Different advantages of Stationary Armature are
- The Output Current can be led directly from fixed terminals on the stators to the load circuits without pass-through brush contacts.
- The stator frame supports the armature core and is built up of laminations.
- it is easier to insulate stationary armature winding for high AC voltages.
- The slip rings are transferred to the low-voltage, low-powered DC field circuit which is also easily insulated.
- The armature windings can be more easily braced to prevent any deformation.
Applications of AC Generators
- AC generators, or alternators, have a wide range of applications in various industries and sectors. Some of the common applications of AC generators are
- AC generators are extensively used in power plants to generate electricity for commercial and residential use.
- AC generators are used in automobiles to generate electricity and recharge the vehicle's battery.
- AC generators are used in construction and mining equipment to power the equipment, including power tools, lighting, and other electrical systems.
- AC generators are used in marine vessels, such as ships and boats, to generate electricity for lighting, navigation, communication, and other onboard systems.
- AC generators are used in aircraft to generate electricity for various systems, including lighting, avionics, and air conditioning.
- AC generators are used as backup power sources in hospitals, and data centres.
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is an AC generator?
How does an AC generator work?
What are the main components of an AC generator?
- Rotor
- Stator
- Slip rings
What is the difference between an AC generator and a DC generator?
How is the frequency of the AC output determined?
What factors affect the voltage output of an AC generator?
- The strength of the magnetic field.
- The number of turns in the coil.
- The speed of rotation of the rotor.
- The load is connected to the generator.
What is the role of slip rings in an AC generator?
How do you regulate the output voltage of an AC generator?
- Varying the speed of the rotor.
- Adjusting the excitation current in the rotor windings.
- Using automatic voltage regulators (AVRs).
What is an automatic voltage regulator (AVR) in an AC generator?
What are the types of AC generators?
- Synchronous generators
- Induction generators
- Brushless generators








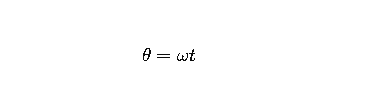






-Electronicsinfos.png)



0 Comments
please do not insert spam links