Three Phase Ac Motor Faults, Remedies
 |
| 3 Phase AC Induction Motor |
The 3-phase AC Induction Motor is known for its efficiency and reliability. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. where a rotating magnetic field is generated by the stator.
The stationary part of the motor induces a current in the rotor. This interaction creates torque, causing the rotor to turn and drive mechanical systems.
The stator contains three-phase windings and is connected to the AC power supply. One of the key advantages of this motor is its self-starting capability. Its robust construction ensures minimal maintenance.
Here are parts of the three-phase AC motor
- Stator
- Rotor
- Stator Windings
- Rotating Magnetic Field
- Synchronous Speed
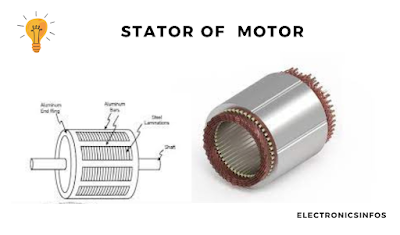
3-phase AC Induction Motor Stator
The 3-phase induction motor stator consists of a steel frame that houses a hollow, cylindrical core made from stacked silicon steel laminations. The purpose of silicon steel laminations is to minimize losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents.
The stator contains numerous slots that hold the three-phase winding circuit, which is connected to the three-phase AC power source. When power is applied, these windings generate a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the rotor to produce torque.
The design of the stator windings is such that they are offset by an electrical angle of 120°.
 |
| 3 Phase AC Induction Motor stator |
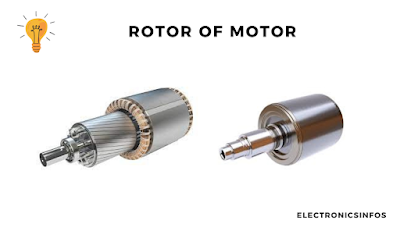
Rotor of 3-phase induction motor
Rotor consists of a cylindrical laminated core, with parallel slots that house conductors, typically made of heavy copper or aluminium bars. These conductors are short-circuited by end rings, and the entire assembly is designed to rotate within the magnetic field.
The unique construction of the rotor, with its skewed slots, not only minimizes magnetic humming noise but also prevents the motor from stalling.
When the stator's rotating magnetic field interacts with the static rotor conductors, an electromotive force (EMF) is induced. The difference in speed between the stator's magnetic field and the rotor's rotation is referred to as slip.
 |
| 3 Phase AC Induction Motor rotor |
Stator Windings
when AC power is applied to the stationary part of the motor, creates a rotating magnetic field. Typically, the windings are made of copper wire and are insulated to prevent electrical shorts.
The common configurations are the star or delta connections. In a star configuration, one end of each winding is connected to a common central point, while the other ends are connected to the power supply.
In contrast, a delta configuration has the ends of the windings connected to form a closed loop, with each junction point connected to the power supply.
This setup is essential for the motor's operation as it generates the rotating magnetic field necessary to induce current in the rotor, thereby creating torque and allowing the motor to turn.
 |
| 3 Phase AC Induction Motor stator winding |
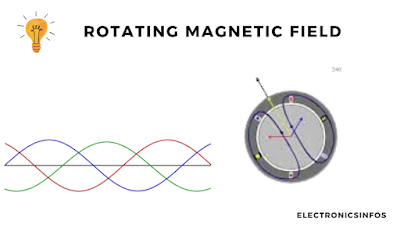
Rotating Magnetic Field
The rotating magnetic field (RMF) is a fundamental concept in the operation of three-phase induction motors. When a three-phase electrical supply is connected to the stator windings of an induction motor, it generates an RMF that moves around the stator.
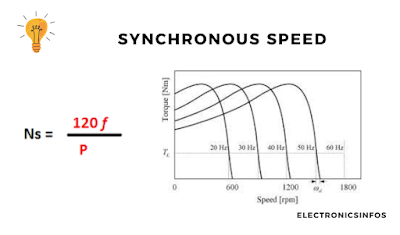
The RMF's speed, known as synchronous speed, is determined by the supply frequency and the number of poles in the motor, following the formula
NS = 120f/P RPM,
where
- f is the frequency and
- P is the number of poles.
 |
| Rotating magnetic field |
Synchronous Speed
 |
| Synchronous speed |
Induction Motor Operation
An induction motor, also known as an asynchronous motor, is a type of alternating current (AC) electric motor that operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
When AC supply is given to the stator, the stationary part of the motor, it generates a rotating magnetic field. This field induces an electric current in the rotor, the moving part of the motor, which in turn produces torque due to the interaction between the magnetic fields of the stator and rotor.
Induction motors are widely used because they are robust, reliable, and require minimal maintenance. They come in various types, primarily single-phase and three-phase motors.
The most common type of three-phase AC motor is the induction motor. The rotating magnetic field in the stator induces currents in the rotor, creating a torque that drives the motor.
The speed at which the rotor rotates is slightly lower than the synchronous speed, creating a "slip" that allows the motor to generate torque.
Types of 3-phase AC Motor
- Squirrel Cage Induction Motor
- Wound Rotor Induction Motor
- Synchronous Motor
Squirrel Cage Induction Motor
The squirrel cage induction motor is a type of induction motor in which rotor windings are made with laminated copper or aluminium slots. the ending point of slots is short with rings. this is the most used induction motor. induction motor is always running below than synchronous speed.
 |
| Squirrel cage induction motor |
Wound Rotor Induction Motor
Synchronous Motor
A synchronous motor is a type of alternating current (AC) motor where the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current.
In these motors, the rotor speed is equal to the speed of the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator. Synchronous motors are highly efficient.
Synchronous motors are widely used in industrial and commercial applications, particularly where low-speed, high-torque drives are required.
Faults In AC Motors
- Mechanical Faults
- Electrical Faults
Mechanical Faults
Mechanical faults are categorized as including
- Improper Bearing operation
- Absence of oil in bearings
- Bent rotor shaft
- Wrong fittings of different Mechanical parts
- Broken side covers of tightening bolts
- Closed cooling ducts
- loose Rotor laminations
- Unbalance Rotor
- Incorrect installation or Foundation of motor
- Breaking of motor fans
- Incorrect Alignment of the rotor
- Incorrect air gap Between stator and rotor
- Breaking the connection box
- Breaking of foundation bolts
- Misalignment of load motor coupling
- Broken Brush Holders Connected With Sliprings
- Broken squirrel cage motor bar
Electrical Faults
Electrical faults are categorized as including
- Open Circuit
- Short Circuit in Complete Windings
- Short Circuited Group
- Punctured insulations
- Wrong connection for specific voltage
- Phase to phase to faults
- Phase to Earth Faults
- Wrong connection in coils
- Loss of contacts in current Carrying parts
- Burning of Slipring
- Open Rotor bars
- Reversed coil
- Reversed pole-phase group
- Reversed-phase
- wrong Grouping
- Short Circuit in core laminations
- Incorrect Size of Windings wire
- Single Phasing
- Unbalanced Phasing
- Unbalanced supply voltage
Faults, Cause and Their Remedies of 3-Phase AC Squirrel Cage Induction Motor
Fault: The motor Fails to start- supply is off
- the fuse was melted
- The supply voltage is not as per the rated voltage
- open circuit faults appeared in the circuit
- open circuit in a starter
- the load is heavy at the motor starting
- The main switch connection is not in the right position
- Bearings are under fault condition
- The motor shaft is skewed
- The overload Relay is tripped.
- The connection of the power circuit was wrong.
- The Motor terminal connection is loose.
- Short circuit or open circuit in the stator winding.
- The motor winding is grounded.
- Check the supply voltage with a multimeter.
- check the fuse and replace it with a higher value.
- check the voltage between the two phases.
Causes
- the motor is running in the two-phase because the third phase is unavailable.
- the open circuit in the winding.
- the connection is loose.
- the air gap is unbalanced in the stator and rotor.
- The motor rotor is not rotated frequently
- The motor belt is tight.
- open circuit in the stator
- Check the supply of three-phase with the help of a Test lamp.
- Check the continuity in the motor terminals with the help of a mager.
- if you find any connection is loose, tighten the connection.
- Check the Motor shaft bearing if it feels loose, change it with a new one.
- check the motor cover if it's tight lose it to rotate the rotor.
- Check the belt condition
- Check the motor stator winding to open the motor, and connect the open wire connection.
shock is felt by touching the motor
Causes
- a ground fault occurs in the motor
- The earth wire is broken.
- Check the motor terminal with the help of a series test lamp if the lamp is on its means wire is connected to the motor frame, disconnect and insulate the connection.
- Check the earth wire continuity with the help of Mager.
The motor does not bear its load
Causes
- The load is heavy
- The motor load belt is tight.
- The short circuit in one of the motor coils.
- The motor winding insulation is weak.
- Regulate the load value.
- Lose the load belt.
- Check the short circuit in the coil. open the coils and check their resistance, the minimum resistance coil is short-circuited.
- varnish the motor winding correctly using any insulating material.
Motor is overheated
Causes
- the connection of the motor is incorrect
- the motor load is heavy
- The supply voltage is low compared to the standard voltage
- the bearing is loose
- the one coil of winding is short
- Check the motor connection and correct the connection.
- Regulate the motor load as per needs.
- Check the supply voltage with the help of a voltmeter.
- Open the side cover and check the bearing position if feels tight replace it with the new one.
- Implement the short circuit test in the coils. the minimum resistance coil is short.
The motor starts up sluggishly
Causes
- The motor stator connection in Star is but they need it in the delta
- One terminal of the motor is connected to the neutral but they need with phase load
- Open the terminal box and accurate their connection.
- Check the motor connection and supply connection
Motor Issues a scratching sound
Causes
- The belt of the motor is loose
- The Motor is overload
- The bearing needs lubricant
- Tight the motor load belt as needed.
- regulate the motor load
- and lubricate the bearing.
Short circuit in a motor circuit
Causes
- The two wires of the motor connected to each other
- Any wire is connected to the main switch
- Check the short circuit test in the coils.
- open the main switch and insulate the non-insulated wire.
Bearing too hot to touch
Causes
- Bearing is dry
- Bearing is tight
- Bearing is loose
- The shaft is skew
- lubricate the bearings
- lose the bearings
- tight the bearings
- checked the shaft position.
Every Third Group In a Three-phase motor is hotter
Causes
- The Resistance of hotted wire is Enough
- The phase is earth
- Due to a short circuit, the wire is hotted, implement the short circuit test and remove the fault or jump to the temporary open coil.
- implement the earth test, remove the earth connection, insulate, and connect again.
- Motor runs hot and explosions accompanied by fire occur in winding.
- Causes
- Due to humidity, the motor faces a temporary short circuit or temporary earth.
Dry the motor winding or insulate it correctly.
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What are common faults in AC motors?
- Overheating
- Bearing failures
- Insulation breakdown
- Rotor faults
- Electrical unbalance
- Voltage fluctuations
What causes overheating in AC motors?
Overloading, poor ventilation, high ambient temperatures, or electrical issues like phase unbalance can lead to overheating.
How can I detect bearing failures in AC motors?
Listen for unusual noises (grinding or squealing), check for excessive vibration, and monitor temperature changes near the bearings.

-Electronicsinfos.png)



0 Comments
please do not insert spam links