Different Methods of Electrical Heating
 |
| Method of Electrical Heating |
There are many examples of electrical heating in our homes i.e Room heater, Electrical geyser, Electrical kettle, Electric iron, Electric toaster, Electrical cooking etc.
Electric heating is also used in industries i.e. Electrical welding, the Baking process of insulators, plastic moulding, heat treatment of electrical conductors etc.
Method of Transfer heat
There are three primary methods of heat transfer including- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between materials. At the molecular level, it occurs when faster-moving, hotter atoms or molecules collide with slower-moving, cooler ones, transferring some of their energy in the process.
 |
| Conduction: Method of heat transfer |
A classic example of conduction is feeling the warmth of a hot coffee cup when you hold it in your hands. The heat from the coffee transfers through the cup to your skin.
The mathematical expression for the conduction of heat can be represented using Fourier's law of heat conduction. Fourier's law states that the rate of heat transfer through a material is proportional to the temperature gradient and can be expressed as
Where:
- q is the rate of heat transfer (in watts or joules per second),
- k is the thermal conductivity of the material (in watts per meter per kelvin),
- A is the cross-sectional area through which heat is transferred (in square meters),
- dT/dx is the temperature gradient (in kelvin per meter) along the direction of heat flow.
This equation describes how heat flows through a material from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature.
Convection
Convection involves the movement of heat by the physical movement of fluids, which can be liquids or gases. In convection, warmer, less dense fluid rises, while cooler, denser fluid sinks, creating a cycle that transfers heat.
 |
| Convection: Method of heat transfer |
This can be observed when boiling water on a stove; the water at the bottom of the pot heats up, becomes less dense, and rises, while cooler water descends to take its place, forming a convective loop.
Where
- Q is the heat transfer rate (in watts),
- h is the convective heat transfer coefficient (in watts per square meter per kelvin),
- A is the surface area through which heat is transferred (in square meters),
- T is the temperature difference between the surface and the fluid (in kelvin).
Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. It does not require a medium to travel through, which means heat can be transferred through the vacuum of space. The most well-known example of radiation is the warmth felt by the sun.
 |
| Radiation: Method of heat transfer |
The sun's rays travel through space and warm the Earth's surface. Similarly, our bodies emit infrared radiation, which is a form of heat transfer.
This law describes the total amount of radiation emitted by an object based on its temperature. The equation is
Where
- Q is the rate of heat transfer by radiation (in watts),
- ε is the emissivity of the object (a dimensionless factor between 0 and 1 that represents its efficiency in emitting radiation),
- σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant 5.67 *10-⁸ watts per square meter per kelvin to the fourth power),
- A is the surface area of the object emitting radiation (in square meters),
- T is the absolute temperature of the object (in Kelvin).
Method Of Heating
Two main types of Heating including
- Resistance Heating
- Induction Heating
Resistance Heating
Resistance heating operates on the principle that when an electric current passes through a conductor, it encounters resistance, which converts electrical energy into heat energy. This method can be direct or indirect.
 |
| Resistance heating: Method of heating |
When Electric current flows in the high resistance material or Element, heat is produced in the material or heating element. the power loss is directly proportional to I²R.
Method Of Resistance Heating
Two ways of Resistance heating including- Direct Resistance Heating
- Indirect Resistance Heating
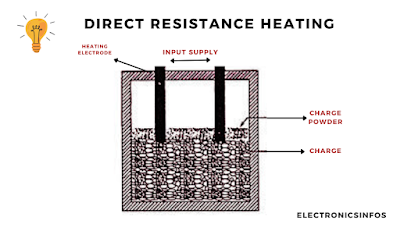
Direct Resistance Heating
Direct Resistance Heating involves passing an electric current directly through the material to be heated, such as in electrode boilers for water heating or resistance welding. The material itself acts as the resistance element, generating heat internally.
The Efficiency of the Direct resistance method is much better compared to the indirect method. This method is mostly used in boilers, resistance welding water heated treatment etc.
 |
| direct Resistance heating: Method of resistance heating |
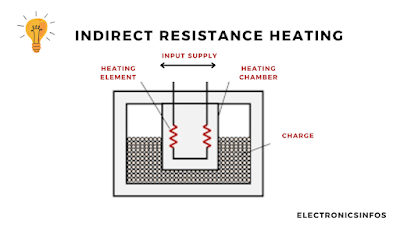
Indirect Resistance Heating
Indirect Resistance Heating uses an external heating element to produce heat, which is then transferred to the material through convection or radiation. Common applications include immersion heaters, ovens, and room heaters.
 |
| Indirect resistance heating: Method of resistance heating |
when the current is flowing in the resistive material the heat is produced which is a direct relation to I²R.
Where
- 'P' is the power dissipated in the material (in watts),
- 'I' is the current flowing through the material (in amperes), and
- 'R' is the resistance of the material (in ohms).
Induction Heating
Advantages of Electrical Heating
- Electrical Heating is a very clean method because there is no ash produced.
- There are no flue or harmful gasses produced in electric heating.
- They need less space.
- There is no need to construct any chimney or to provide extra installation.
- The temperature is controlled manually or automatically in electrical heating.
- Special Heating requirements such as Uniform heating of a material or need for heat in a specific point of the object are only possible in Electrical Heating.
- Electrical heating is a very efficient method.
- Electrical Heating produces no irritating noises.
- if we need uniform heat for non-electric objects like plastic, wood and bakery items we can use the electric heating method because it's the most suitable method to heat the objects.
- Electrical Heating is a very protective method because we easily control it with the help of switchgear.
- Electrical heating needs less attention and the running cost is also low.
- Labour charges are also small compared to other forms of heating.
Disadvantages of Electrical Heating
- The initial cost of Electrical heating is high.
- Electric heating relies solely on electricity, which can be a problem during power outages.
- In areas where electricity costs are high, electric heating becomes uneconomic.
- The cost of electric heating can fluctuate with changes in electricity prices, which can be unpredictable.
- we need high Electric insulation and high thermal insulation.
- There is a risk of electrical hazards such as electric shock, fire, arc flash, or explosion.
- If the electricity is generated from fossil fuels, it can have a significant carbon footprint.
- The chance of oxidation is available.
- Energy can be lost in transmission from the power plant to the home, reducing overall efficiency.
- Some electric heating systems may take longer to heat up spaces compared to other methods.
- some electric heating systems may still require space for components like boilers or radiators.
- The electrical heating systems need skilled labour.
Applications of Electrical Heating
- Electrical heating is used in Space heating, water heating, and radiant floor heating in homes.
- Electrical heating is used in Cooking appliances like electric stoves and ovens.
- it is used in Water heaters for domestic hot water supply.
- it is used in Electric blankets and space heaters for warmth.
- it is used in Industrial heating for manufacturing processes, food production, and material processing.
- Electric stoves, ovens, and cooktops in commercial kitchens.
- Melting metals for extraction or purification processes.
- Electric furnaces and heat pumps for heating and cooling in buildings.
- Drying of paint on manufactured items through infrared heating.
- it is used in Laboratory equipment, heated pipelines, and heat tracing systems.
- it is used in Heat treatment of metals, such as hardening, annealing, and tempering.Enamelling of copper conductors.
Conclusions
Electrical heating, the process of converting electrical energy into heat energy, is a highly efficient method with nearly 98 % efficiency in energy conversion.
These methods have diverse applications, from domestic water heating to industrial metal treatment. However, it's important to consider the cost of electricity and the insulation of the space to maximize efficiency.


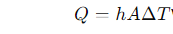





-Electronicsinfos.png)

0 Comments
please do not insert spam links